Small Hedges, Big Wins: Here’s How Micro-Hedging Beats the Blanket Approach
In the volatile world of forex, the ability to manage risk and protect profits can make the difference between a company thriving or struggling. Traditional hedging strategies, often based on bulk or blanket approaches, are widely used to shield businesses from adverse currency fluctuations. However, while these methods may seem efficient on the surface, they can lead to over-hedging, cash flow mismatches, and missed opportunities, especially in a fast-paced, unpredictable market.
This is where micro-hedging shines. Unlike blanket hedging, which uses a one-size-fits-all approach for a company’s overall currency exposure, micro-hedging focuses on more specific, targeted transactions, invoices, or exposures. By adopting a micro-hedging strategy, businesses can navigate forex risk with precision, enhance cash flow alignment, and lock in better rates.
Why Blanket Hedging Can Lead to Problems
Traditional bulk hedging is like throwing a wide net to protect against any and all currency movements. It involves using broad, company-wide hedges to cover all foreign exchange exposure. While this might seem like an easy way to mitigate risk, it can cause several issues:
Over-Hedging
When a company hedges all of its foreign currency exposure, it often ends up over-hedging. This occurs when hedges are placed on transactions that don't necessarily need protection. Over-hedging ties up capital and limits potential gains, especially when currency movements are favorable.
Example:
You expect €200,000 and hedge it at ₹91.
Later, you only receive €150,000.
You still need to buy the extra €50,000 at the current rate of ₹90.
Loss = ₹1 × 50,000 = ₹50,000
Always hedge confirmed amounts—extra hedging can cost you.
Cash Flow Mismatches
A blanket hedge might not align with the timing of cash flows.
For Example:
An export company expects to receive $300,000 in 60 days, but it hedges today at ₹85.00.
After 60 days, the spot rate is ₹86.20—much better than the hedge.
Missed gain = ₹1.20 × 300,000 = ₹3,60,000
If they had timed the hedge better, they could’ve earned more. Match your hedge with your actual payment or receipt date to avoid locking in poor rates.
Lost Opportunities
With blanket hedging, the company often locks in rates across the board, even for transactions that don’t require hedging. If a currency pair experiences favorable movement, the company may be unable to benefit from it, thereby reducing potential profits.
Example:
A company hedges its entire $500,000 export at ₹84.50.
But when the payment comes in, the market rate is ₹86.00.
Because of the hedge, they miss out on the better rate.
Missed profit = ₹1.50 × 500,000 = ₹7,50,000
In such cases, micro-hedging (hedging in smaller parts and closer to actual dates) gives you more flexibility to benefit from good market moves.
These challenges become particularly prominent in volatile markets where timing, precision, and flexibility are critical.
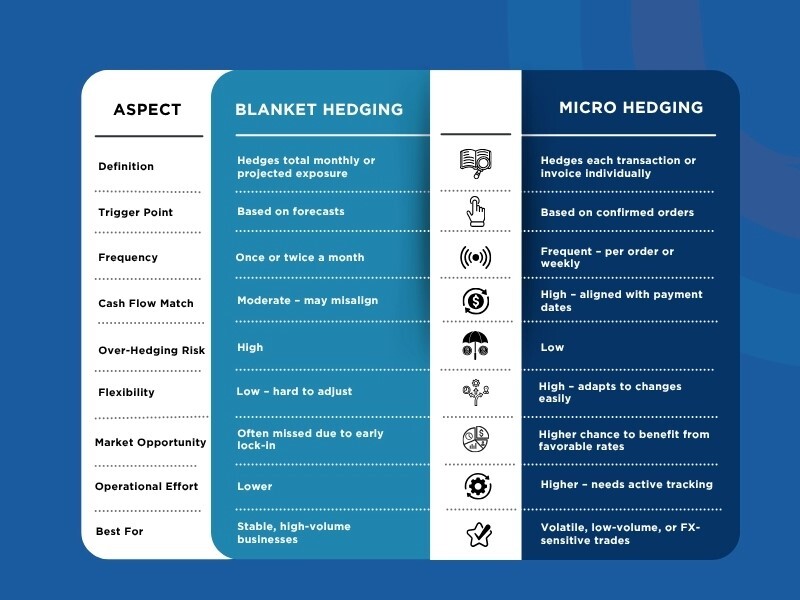
Understanding Hedging Approaches: Micro vs. Aggregate
|
Aspect |
Monthly Bucket Hedging |
Micro Hedging (Order-wise) |
|
Definition |
Hedges the total projected exposure for the month in aggregate |
Hedges each export/import order individually as it arises |
|
Hedging Trigger |
Based on monthly forecast or booking data |
Triggered per confirmed order or invoice |
|
Granularity |
Aggregated exposure |
Highly granular, order-level |
|
Hedging Frequency |
Usually once or twice per month |
Frequent, sometimes daily or weekly |
|
Operational Effort |
Lower – fewer hedge contracts |
Higher – requires active tracking and execution |
|
Flexibility |
Less flexible once booked |
Very flexible – adapts to order volume/timing changes |
|
Suitability |
Best for companies with predictable flows and bulk billing |
Ideal for companies with volatile or irregular order patterns |
|
Risk Coverage |
Covers net exposure – may have under/over-hedging risks |
Closer to actual cash flow, so more accurate hedging |
|
Cost of Hedging |
Lower – fewer contracts and lower admin cost |
Slightly higher – more trades, possible higher bank charges |
|
Documentation Burden |
Minimal – fewer contracts to reconcile |
More effort in mapping hedges to underlying orders |
|
MTM/Accounting Complexity |
Easier – fewer entries in books |
More complex – multiple hedge contracts to reconcile individually |
|
Forecast Dependency |
High – depends on good monthly projections |
Low – based on confirmed orders only |
|
Best For |
High-volume exporters/importers, predictable billing, bulk trades |
Low-volume/project-based, FX-sensitive pricing, high-margin trades |
Micro-Hedging: Targeting Specific Exposures with Precision
Micro-hedging is about focusing on specific transactions, invoices, or exposures, rather than blanket hedging for the entire company. It enables businesses to target their hedging efforts where they are most needed. Here’s how it works:
Precision
Micro-hedging involves targeting specific risks, such as a single invoice or shipment, rather than hedging for broad exposure. By focusing on individual transactions, companies can hedge exactly when necessary, minimizing excess hedging.
Timing Flexibility
In volatile markets, timing is everything. Micro-hedging provides the flexibility to hedge only when required, aligning perfectly with cash flow and payment schedules. This means companies can lock in favorable exchange rates when they’re most advantageous and avoid locking in unfavorable rates on less critical transactions.
Cash Flow Alignment
With micro-hedging, hedging is aligned with specific invoices or payments. This minimizes mismatches between hedging and actual cash flows, ensuring that the hedge provides the desired protection without affecting liquidity.
By strategically targeting specific exposures, businesses can save money on unnecessary hedging costs while ensuring they’re protected where it matters most.
Scenarios Where Micro-Hedging Outperforms
Micro-hedging is especially effective in the following scenarios:
Staggered Shipments
When shipments are scheduled over a period of time, each one may be exposed to different currency risks. Micro-hedging allows companies to hedge the currency exposure on each shipment separately, ensuring that each hedge is tailored to the specific time frame and currency risk involved.
For Example:
A company exports goods in 3 shipments of $100,000 each over 3 months.
Instead of hedging the full $300,000 at once, they hedge:
- Month 1 at ₹84.50
- Month 2 at ₹85.50
- Month 3 at ₹86.50
This way, they lock in better rates for later payments.
If they had used a blanket hedge at ₹84.50 for all, they would’ve missed out on higher rates in Month 2 and 3.
Milestone-Based Payments
For companies that deal with projects paid in milestones, such as construction or large-scale manufacturing projects, micro-hedging provides precision in timing. The company can hedge each payment based on the project milestones, aligning the hedge with the specific cash flow event.
If a company is paid in multiple installments over a year, hedging each payment individually allows for better alignment with exchange rate fluctuations, reducing the risk of locking in unfavorable rates early on.
Volatile Currencies
In markets where currency volatility is high, such as with emerging market currencies, micro-hedging allows companies to adjust their strategy quickly. This flexibility is crucial because it enables businesses to hedge specific exposures when volatility is expected to be high or when currency movements are particularly unpredictable.
For instance:
A company has a total exposure of $600,000 and decides to hedge in steps:
- Hedge 30% when USDINR hits ₹84.00
- Hedge another 40% at ₹85.00
- Hedge the remaining 30% at ₹86.00
Let’s say the market moves as expected:
- 30% at ₹84.00 = $180,000
- 40% at ₹85.00 = $240,000
- 30% at ₹86.00 = $180,000
Average hedged rate = ₹85.00
If they had done a blanket hedge at the start at ₹84.00, they would’ve missed the higher rates.
Extra gain = ₹6,00,000
Low-Margin Businesses
For low-margin industries, small fluctuations in currency rates can significantly affect profitability. Micro-hedging allows these companies to target their most critical transactions, ensuring that they are protected against major currency fluctuations without locking in unnecessary costs.
Advantages of Micro-Hedging
Better Rate Locking
By focusing on individual transactions or exposures, micro-hedging allows companies to lock in the most favorable exchange rates at the most opportune times. This can result in substantial savings, particularly in volatile markets.
Minimized Risk
Micro-hedging reduces the risk of over-hedging, which can be costly. By focusing only on the most critical exposures, companies can ensure they are protected without tying up unnecessary capital in hedging.
Reduced Cost of Hedging
Since micro-hedging targets only the essential exposures, companies avoid unnecessary hedge costs. This makes it a more cost-effective approach compared to blanket hedging.
Recommendations for Implementing Micro-Hedging
To effectively implement micro-hedging, companies should:
- Assess their specific currency risks: Identify the transactions that are most exposed to currency fluctuations and prioritize those for hedging.
- Use advanced forex tools: Leverage hedging instruments like forward contracts, options, and swaps that allow for flexibility and precision.
- Regularly review hedging strategies: Monitor market conditions and adjust the hedging strategy based on evolving currency movements and cash flow patterns.
- Collaborate with a forex advisor: Work with an expert who can guide the business through the complexities of micro-hedging, ensuring maximum cost savings and minimal risk.
Conclusion
In today’s volatile forex market, micro-hedging offers businesses a powerful tool to navigate currency risks with precision. Unlike blanket hedging, which can lead to over-hedging and cash flow mismatches, micro-hedging allows companies to target specific exposures, align with cash flow schedules, and lock in better exchange rates. Whether dealing with staggered shipments, milestone-based payments, or volatile currencies, micro-hedging enables businesses to protect their profits while maintaining flexibility and control. By adopting this targeted strategy, companies can achieve big wins in the forex market with small, well-placed hedges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is micro-hedging in forex?
Micro-hedging involves targeting specific transactions, invoices, or exposures to hedge currency risk with precision, instead of using blanket hedging for the entire business.
2. How does micro-hedging differ from traditional hedging?
Traditional hedging uses a broad approach to hedge all currency exposure, while micro-hedging focuses on individual transactions, providing greater flexibility and precision.
3. When should I use micro-hedging?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nullam tempor arcu
Micro-hedging is ideal for businesses with staggered shipments, milestone-based payments, low-margin operations, or in markets with volatile currencies.
non commodo elementum.